39 时间序列回归
39.1 随机波动率模型
随机波动率模型主要用于股票时间序列数据建模。本节以美团股价数据为例介绍随机波动率模型,并分别以 Stan 框架和 fGarch 包拟合模型。
# 美团上市至 2023-07-15
meituan <- readRDS(file = "data/meituan.rds")
library(zoo)
library(xts)
library(ggplot2)
autoplot(meituan[, "3690.HK.Adjusted"]) +
theme_classic() +
labs(x = "日期", y = "股价")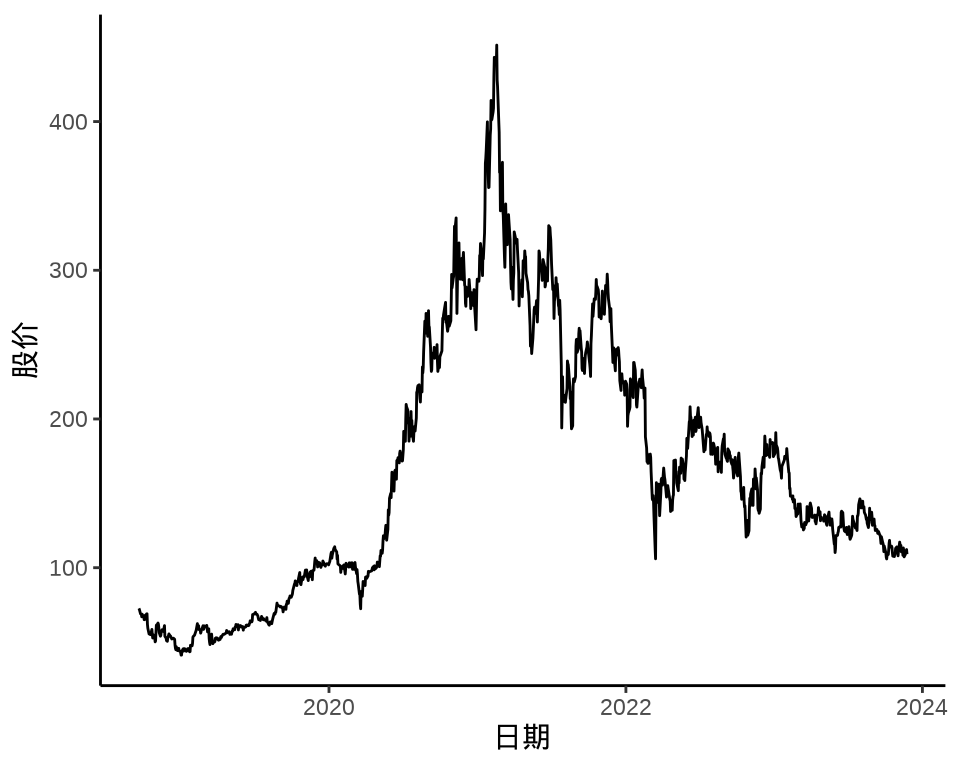
对数收益率的计算公式如下:
\[ \mathrm{对数收益率} = \ln(\mathrm{今日收盘价} / \mathrm{上一收盘价} ) = \ln (1 + \mathrm{普通收益率}) \]
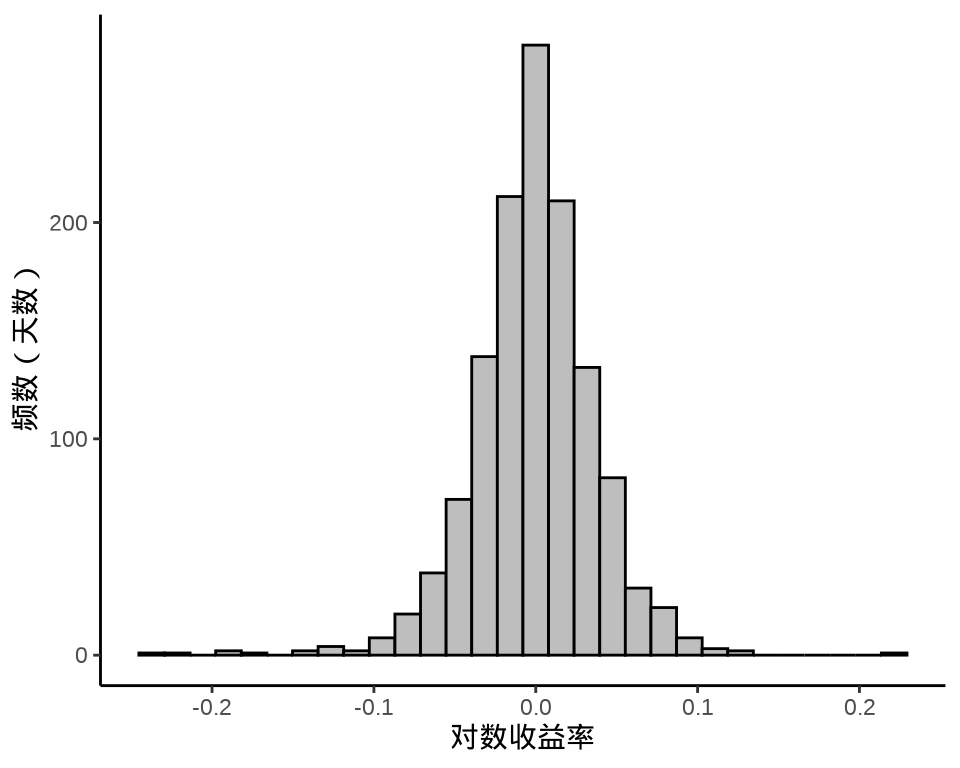
下图给出股价对数收益率变化和股价对数收益率的分布,可以看出在不同时间段,收益率波动幅度是不同的,美团股价对数收益率的分布可以看作正态分布。
meituan_log_return <- log(1 + diff(meituan[, "3690.HK.Adjusted"]) / meituan[, "3690.HK.Adjusted"])[-1,]
autoplot(meituan_log_return) +
theme_classic() +
labs(x = "日期", y = "对数收益率")
ggplot(data = meituan_log_return, aes(x = `3690.HK.Adjusted`)) +
geom_histogram(color = "black", fill = "gray", bins = 30) +
theme_classic() +
labs(x = "对数收益率", y = "频数(天数)")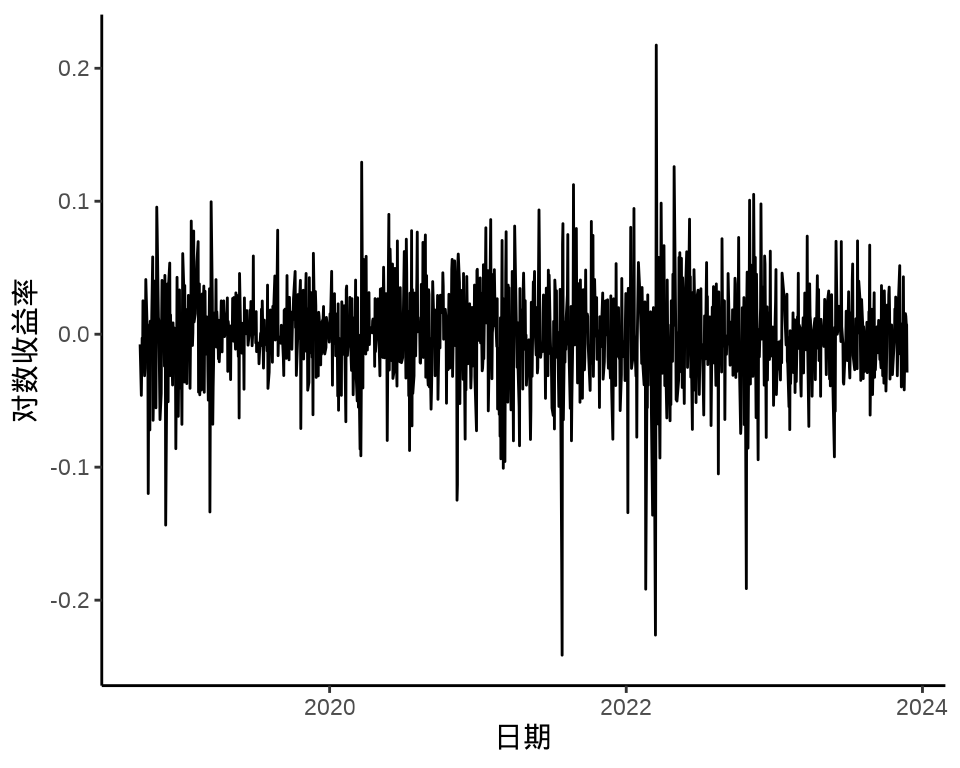
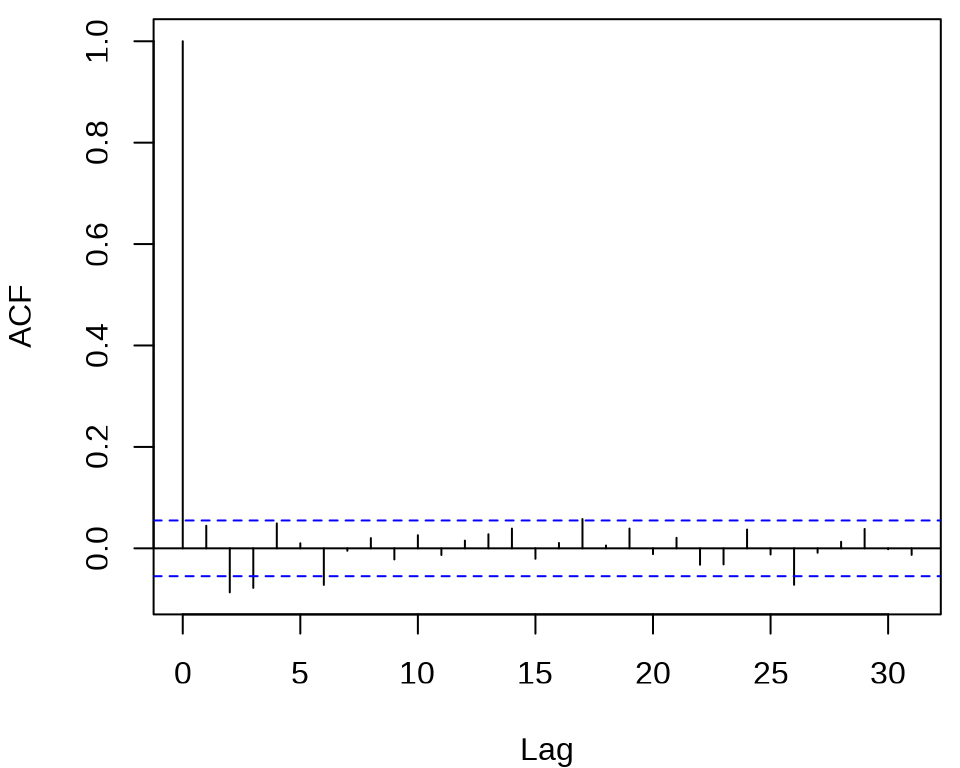
检查对数收益率序列的自相关图
发现,滞后 2、3、6、26 阶都有出界,滞后 17 阶略微出界,其它的自相关都在零水平线的界限内。
#>
#> Box-Ljung test
#>
#> data: meituan_log_return
#> X-squared = 32.367, df = 12, p-value = 0.001214在 0.05 水平下拒绝了白噪声检验,说明对数收益率序列存在相关性。同理,也注意到对数收益率的绝对值和平方序列都不是独立的,存在相关性。
#>
#> Box-Ljung test
#>
#> data: (meituan_log_return - mean(meituan_log_return))^2
#> X-squared = 113.76, df = 12, p-value < 2.2e-16结果高度显著,说明有 ARCH 效应。
39.1.1 Stan 框架
39.1.2 fGarch 包
《金融时间序列分析讲义》两个波动率建模方法
- 自回归条件异方差模型(Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity,简称 ARCH)。
- 广义自回归条件异方差模型 (Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity,简称 GARCH )
确定 ARCH 模型的阶,观察残差的平方的 ACF 和 PACF 。
acf((meituan_log_return - mean(meituan_log_return))^2, main = "")
pacf((meituan_log_return - mean(meituan_log_return))^2, main = "")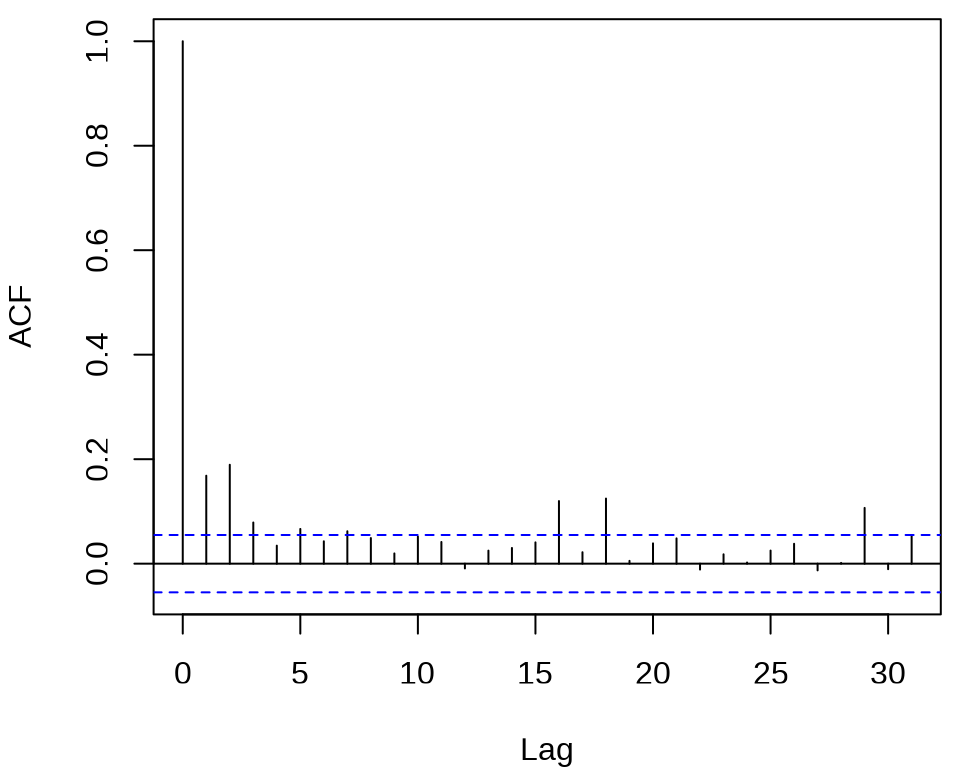
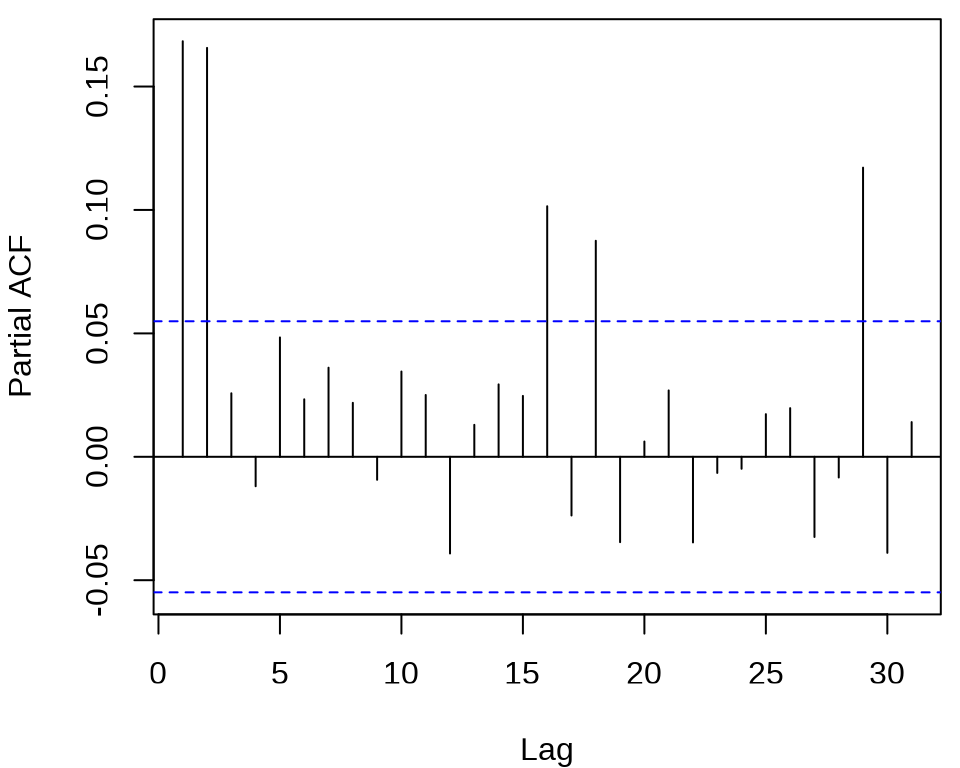
发现 ACF 在滞后 1、2、3 阶比较突出,PACF 在滞后 1、2、16、18、29 阶比较突出。所以下面先来考虑低阶的 ARCH(2) 模型,设 \(r_t\) 为对数收益率。
\[ \begin{aligned} r_t &= \mu + a_t, \quad a_t = \sigma_t \epsilon_t, \quad \epsilon_t \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1) \\ \sigma_t^2 &= \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 a_{t-1}^2 + \alpha_2 a_{t-2}^2. \end{aligned} \]
拟合 ARCH 模型,比较模型估计结果,根据系数显著性的结果,采纳 ARCH(2) 模型。
library(fGarch)
meituan_garch1 <- garchFit(~ 1 + garch(2, 0), data = meituan_log_return, trace = FALSE, cond.dist = "std")
summary(meituan_garch1)#>
#> Title:
#> GARCH Modelling
#>
#> Call:
#> garchFit(formula = ~1 + garch(2, 0), data = meituan_log_return,
#> cond.dist = "std", trace = FALSE)
#>
#> Mean and Variance Equation:
#> data ~ 1 + garch(2, 0)
#> <environment: 0x5579d2fa0248>
#> [data = meituan_log_return]
#>
#> Conditional Distribution:
#> std
#>
#> Coefficient(s):
#> mu omega alpha1 alpha2 shape
#> -5.6632e-05 1.0704e-03 1.1555e-01 1.4380e-01 4.8131e+00
#>
#> Std. Errors:
#> based on Hessian
#>
#> Error Analysis:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> mu -5.663e-05 8.881e-04 -0.064 0.94915
#> omega 1.070e-03 9.507e-05 11.260 < 2e-16 ***
#> alpha1 1.156e-01 4.299e-02 2.688 0.00719 **
#> alpha2 1.438e-01 4.754e-02 3.025 0.00249 **
#> shape 4.813e+00 6.561e-01 7.336 2.2e-13 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Log Likelihood:
#> 2459.91 normalized: 1.930856
#>
#> Description:
#> Sun Dec 10 15:29:12 2023 by user:
#>
#>
#> Standardised Residuals Tests:
#> Statistic p-Value
#> Jarque-Bera Test R Chi^2 632.2496448 0.000000e+00
#> Shapiro-Wilk Test R W 0.9648585 0.000000e+00
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(10) 19.3876684 3.560618e-02
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(15) 23.5920804 7.235243e-02
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(20) 33.2714312 3.149690e-02
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(10) 12.6594516 2.433403e-01
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(15) 25.3895008 4.495082e-02
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(20) 57.7893864 1.556847e-05
#> LM Arch Test R TR^2 17.7056006 1.249263e-01
#>
#> Information Criterion Statistics:
#> AIC BIC SIC HQIC
#> -3.853862 -3.833650 -3.853893 -3.846271函数 garchFit() 的参数 cond.dist 默认值为 "norm" 表示标准正态分布,cond.dist = "std" 表示标准 t 分布。模型均值的估计值接近 0 是符合预期的,且显著性没通过,对数收益率在 0 上下波动。将估计结果代入模型,得到
\[ \begin{aligned} r_t &= -5.665 \times 10^{-5} + a_t, \quad a_t = \sigma_t \epsilon_t, \quad \epsilon_t \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1) \\ \sigma_t^2 &= 1.070 \times 10^{-3} + 0.1156 a_{t-1}^2 + 0.1438a_{t-2}^2. \end{aligned} \]
下面考虑 GARCH(1,1) 模型
\[ \begin{aligned} r_t &= \mu + a_t, \quad a_t = \sigma_t \epsilon_t, \quad \epsilon_t \sim \mathcal{N}(0,1) \\ \sigma_t^2 &= \alpha_0 + \alpha_1 a_{t-1}^2 + \beta_1 \sigma_{t-1}^2. \end{aligned} \]
meituan_garch2 <- garchFit(~ 1 + garch(1, 1), data = meituan_log_return, trace = FALSE, cond.dist = "std")
summary(meituan_garch2)#>
#> Title:
#> GARCH Modelling
#>
#> Call:
#> garchFit(formula = ~1 + garch(1, 1), data = meituan_log_return,
#> cond.dist = "std", trace = FALSE)
#>
#> Mean and Variance Equation:
#> data ~ 1 + garch(1, 1)
#> <environment: 0x5579d0431d08>
#> [data = meituan_log_return]
#>
#> Conditional Distribution:
#> std
#>
#> Coefficient(s):
#> mu omega alpha1 beta1 shape
#> -8.6653e-05 3.4394e-05 5.8249e-02 9.1819e-01 5.2787e+00
#>
#> Std. Errors:
#> based on Hessian
#>
#> Error Analysis:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> mu -8.665e-05 8.641e-04 -0.100 0.92012
#> omega 3.439e-05 1.866e-05 1.843 0.06529 .
#> alpha1 5.825e-02 1.788e-02 3.257 0.00113 **
#> beta1 9.182e-01 2.667e-02 34.434 < 2e-16 ***
#> shape 5.279e+00 7.517e-01 7.023 2.18e-12 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
#>
#> Log Likelihood:
#> 2478.786 normalized: 1.945672
#>
#> Description:
#> Sun Dec 10 15:29:12 2023 by user:
#>
#>
#> Standardised Residuals Tests:
#> Statistic p-Value
#> Jarque-Bera Test R Chi^2 523.6362720 0.0000000
#> Shapiro-Wilk Test R W 0.9666878 0.0000000
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(10) 14.4633761 0.1528851
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(15) 18.5039288 0.2370994
#> Ljung-Box Test R Q(20) 27.4217443 0.1238100
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(10) 8.7555217 0.5554521
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(15) 10.6532128 0.7767678
#> Ljung-Box Test R^2 Q(20) 23.7435667 0.2537732
#> LM Arch Test R TR^2 10.1204846 0.6053914
#>
#> Information Criterion Statistics:
#> AIC BIC SIC HQIC
#> -3.883494 -3.863283 -3.883525 -3.875903波动率的贡献主要来自 \(\sigma_{t-1}^2\) ,其系数 \(\beta_1\) 为 0.918。通过对数似然的比较,可以发现 GARCH(1,1) 模型比 ARCH(2) 模型更好。
39.2 贝叶斯可加模型
大规模时间序列回归,观察值是比较多的,可达数十万、数百万,乃至更多。粗粒度时时间跨度往往很长,比如数十年的天粒度数据,细粒度时时间跨度可短可长,比如数年的半小时级数据,总之,需要包含多个季节的数据,各种季节性重复出现。通过时序图可以观察到明显的季节性,而且往往是多种周期不同的季节性混合在一起,有时还包含一定的趋势性。举例来说,比如 2018-2023 年美国旧金山犯罪事件报告数据,事件数量的变化趋势,除了上述季节性因素,特殊事件疫情肯定会影响,数据规模约 200 M 。再比如 2018-2023 年美国境内和跨境旅游业中的航班数据,原始数据非常大,R 包 nycflights13 提供纽约机场的部分航班数据。
39.2.1 Stan 框架
39.2.2 INLA 框架
模型内容、成分结构和参数解释
阿卜杜拉国王科技大学(King Abdullah University of Science and Technology 简称 KAUST)的 Håvard Rue 等开发了 INLA 框架 (Rue, Martino, 和 Chopin 2009)。INLA 动态时间序列建模 (Nalini Ravishanker 和 Soyer 2022)
39.3 一些非参数模型
39.3.1 mgcv 包
模型内容、成分结构和参数解释。一般可加模型,在似然函数中添加平滑样条,与 Lasso 回归模型在形式上有相似之处,属于频率派方法。
mgcv 包 (S. N. Wood 2017) 是 R 软件内置的推荐组件,由 Simon Wood 开发和维护,历经多年,成熟稳定。对于时间序列数据预测,数万和百万级观测值都可以 (Simon N. Wood, Goude, 和 Shaw 2015)。函数 bam()
39.3.2 nnet 包
多层感知机是一种前馈神经网络,nnet 包的函数 nnet() 实现了单隐藏层的简单神经网络。
39.3.3 tensorflow 框架
前面介绍的模型都具有非常强的可解释性,比如各个参数对模型的作用。对于复杂的时间序列数据,比较适合用复杂的模型来拟合,看重模型的泛化能力,而不那么关注模型的机理。下面用 LSTM (长短期记忆)神经网络来训练时间序列数据,预测未来一周的趋势。
forecastML 采用机器学习方法可以一次向前预测多期。
39.4 习题
-
基于 R 软件内置的数据集
sunspots和sunspot.month比较 INLA 和 mgcv 框架的预测效果。代码
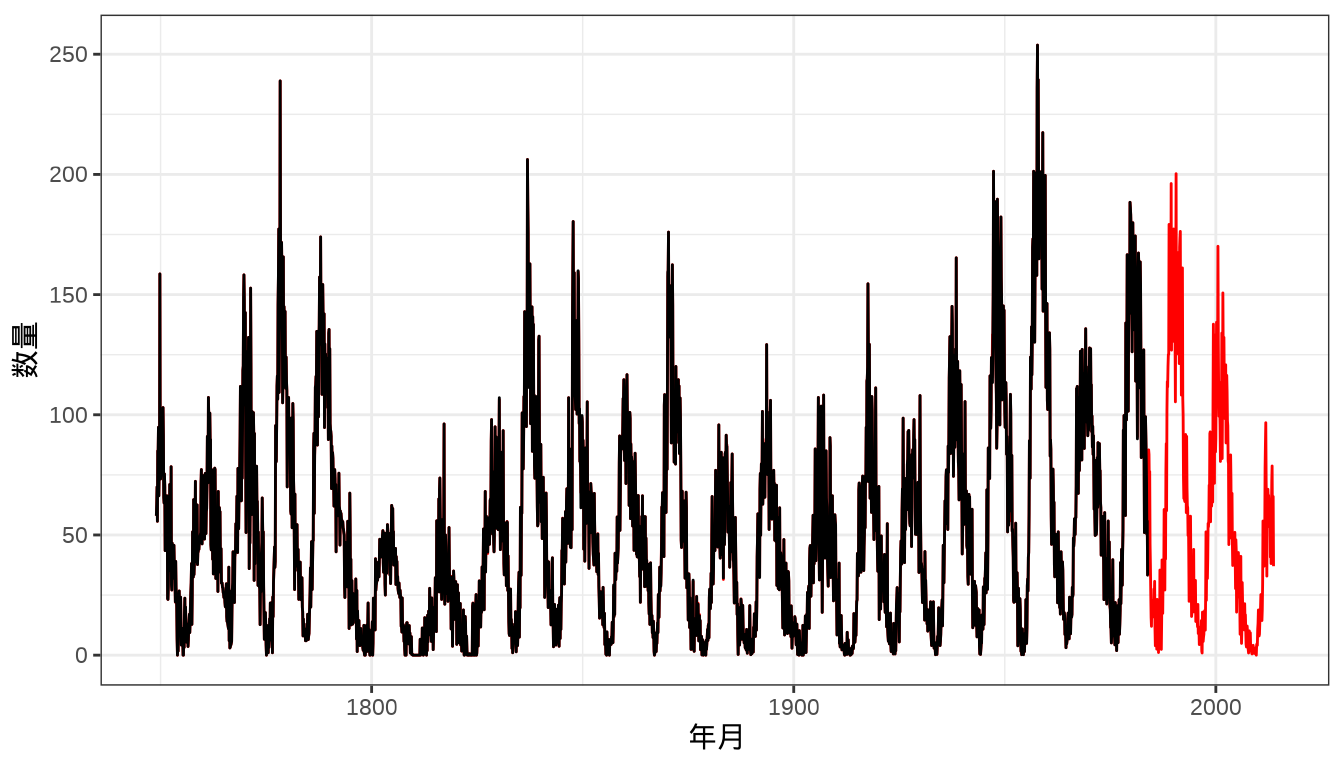
图 39.5: 预测月粒度太阳黑子数量 图中黑线和红线分别表示 1749-1983 年、1984-2014 年每月太阳黑子数量。